Madhuca longifolia
Read community contributed articles on biodiversity & environment || Cultural practices & mythological stories related to Indian biodiversity || Official documents related to environment || NGOs, Blogs and Websites || Environment-related video collection || Plants of India || Mammals of India || Facebook || Twitter
Share this page: Madhuca longifolia
Madhuca longifolia, commonly known as mahwa or mahua, is an Indian tropical tree found largely in the central and north Indian plains and forests. It is a fast growing tree that grows to approximately 20 meters in height, possesses evergreen or semi-evergreen foliage, and belongs to the family Sapotaceae. It is adapted to arid environments, being a prominent tree in tropical mixed deciduous forests in India in the states of Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Gujarat and Orissa (Source: Wikipedia)
Click here to see all Semantic Properties associated with this page
Please note that the above slideshow is automatically created by searching Flickr and does not contain manually curated images. Hence, it is likely that some images may not be exactly of Madhuca longifolia.
Click on the tabs below to know more...
- Species identity and nomenclature
- Current Wikipedia entry
- Binomial Classification
- Morphological features
- Habitat and Geographical Spread
- Maps
- Medicinal Importance
- Cultural significance
- Commercial importance and cultivation
- Summary of PubMed articles
- Summary of NCBI molecular data
- External Links
- Images and Videos
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Names of users who have contributed to this species page | shwetankverma, gauravm | |
| Date on which this page was first created | 2010/08/08 | |
| This page was last modified on: | 24 November 2010 05:11:33 | |
| Name of the species | Madhuca longifolia | |
| ID on Encyclopedia of Life | 1155126 | |
| Synonyms | Please check Binomial Classification section for synonyms. | |
| Common English Names | Mahua | |
| Common Hindi Names | महुआ Mahua | |
| Common Indian names | Mahua (Bengali);
Mahua, Mahudo (Gujarati); Mahua (Hindi); Halippe,Hippe, Ippe, Movaro (Kannada); Illippa, Pooma (Malayalam); Mahua, Mohwa (Marathi); Illupei (Tamil); Ippa (Telugu) |
Shwetankverma |
| Origins/Meanings of the common names |
Taxonomy from Encyclopedia of Life
If nothing is displayed in this section, it means the EoL ID has not been defined. Please click on Edit with form button on top and follow the instructions for filling in the EoL ID
{{#EoLOnlyHierarchy:1155126}}
Taxonomy filled in form
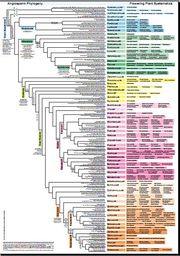
Click here for the PDF of the phylogeny
| Taxon | Value |
|---|---|
| Regnum (Kingdom) | Plantae |
| Division | Magnoliophyta |
| Class | Magnoliopsida |
| Order | Ericales |
| Family | Sapotaceae |
| Genus | Madhuca |
| Source of data | ' |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Division | Taxon details | Taxon morphology details |
|---|---|---|
| Magnoliophyta | Also called Angiospermae. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 140 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 100 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60-100 million years ago. | These are seed plants like Gymnosperms, but can be differentiated by the presence of flowers, seeds containing endosperm and seeds that produce a fruit. Angiosperms are the most diverse and highly evolutionarily successful group of land plants. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Taxon details | Taxon morphology details |
|---|---|---|
| Magnoliopsida | Magnoliopsida is the scientific name for dicots. This class contains about ~1,99,350 species of Angiosperms. Eudicots are a subset of Dicots. Based on chloroplast DNA sequences, the divergence date between monocots and dicots is estimated to be ~200 million years, with a 40 million years uncertainty. | Dicots are diverse in habit, with half of all the species being more or less woody-stemmed - a reflection of the usual presence of a vascular cambium in the class. Annuals, biennials, vines, epiphytes, aquatics, parasites, and saprotrophs are also well represented in dicots. Vascular bundles of the stem are usually borne in a ring that encloses the pith. Vessel elements present except in some putatively primitive woody or aquatic families. Most dicots have a primary root system derived from the radicle, although some have an adventitious root system commonly seen in the class of monocots. Cotyledons are usually 2, seldom 1, 3, or 4. Leaves are mostly net-veined. |
|
|
| Family | Taxon details | Taxon morphology details |
|---|---|---|
| Sapotaceae | Trees or shrubs , usually producing latex. Leaves spirally arranged or alternate and distichous, rarely ± opposite, sometimes crowded at apex of branchlets ; stipules early deciduous or absent; leaf blade papery or leathery, margin entire. Flowers bisexual or unisexual , usually in sessile axillary clusters , rarely solitary; cluster pedunculate or in raceme-like inflorescence, bracteolate . Calyx a single whorl of usually 4--6 sepals, or 2 whorls each with 2--4 sepals. Corolla lobes as many to 2 X as many as sepals, usually entire, rarely with 2 lacerate or lobular appendages . Stamens inserted at corolla base or at throat of corolla tube , as many as and opposite corolla lobes to many and in 2 or 3 whorls; staminodes when present alternate with stamens, scaly to petal-like. Ovary superior, 4- or 5-locular, placentation axillary; ovules 1 per locule, anatropous . Style 1, often apically lobed . Fruit a berry or drupe, 1- to many-seeded. Seed coat brown (pale yellow in Pouteria annamensis), hard, shiny, rich in tannin; endosperm usually oily; seed scar lateral and linear to oblong or basal and round. |
|
Based on classification
| Family | Taxon details | Taxon morphology details |
|---|---|---|
| Sapotaceae | Trees or shrubs , usually producing latex. Leaves spirally arranged or alternate and distichous, rarely ± opposite, sometimes crowded at apex of branchlets ; stipules early deciduous or absent; leaf blade papery or leathery, margin entire. Flowers bisexual or unisexual , usually in sessile axillary clusters , rarely solitary; cluster pedunculate or in raceme-like inflorescence, bracteolate . Calyx a single whorl of usually 4--6 sepals, or 2 whorls each with 2--4 sepals. Corolla lobes as many to 2 X as many as sepals, usually entire, rarely with 2 lacerate or lobular appendages . Stamens inserted at corolla base or at throat of corolla tube , as many as and opposite corolla lobes to many and in 2 or 3 whorls; staminodes when present alternate with stamens, scaly to petal-like. Ovary superior, 4- or 5-locular, placentation axillary; ovules 1 per locule, anatropous . Style 1, often apically lobed . Fruit a berry or drupe, 1- to many-seeded. Seed coat brown (pale yellow in Pouteria annamensis), hard, shiny, rich in tannin; endosperm usually oily; seed scar lateral and linear to oblong or basal and round. |
More details can be found in the Binomial Classification section.
Morphology from Encyclopedia of Life
If nothing is displayed in this section, it means the EoL ID has not been defined. Please click on Edit with form button on top and follow the instructions for filling in the EoL ID
{{#EoLOnlyDescription:1155126}}
General morphology
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| General morphological features of the plant |
| Seed dispersal mechanism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bloom type | ||
| Life cycle of the plant |
How to identify this species
For a detailed description, refer to the General Morphology details above
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Type of plant | Woody (Tree/Shrub) | |
| Plant height | More than 10 feet | Google images, Wikipedia |
| Flower color | Brown | |
| Flower shape | ||
| Floral symmetry | ||
| Phyllotaxy of leaves | ||
| Leaf shape | ||
| Is the leaf petiolated or sessile? | ||
| Is the leaf simple or compound? |
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| IUCN Conservation Status | Not Evaluated | EoL |
| Indian States in which the species has been documented | Andhra Pradesh,Bihar,Chhatisgarh,Gujarat,Jharkhand,Karnataka,Kerala,Madhya Pradesh,Maharashtra,Orissa,Rajasthan,Tamil Nadu,West Bengal | Wiki / plant databse of india |
| Locations at which the species has been documented | ||
| Biotic zones inhabited | East Coast, Indo-Gangetic Plain | |
| Details about the habitat | ||
| Is this species native to India? | Yes | |
| Is the species indigenous/endemic to Sub-Himalayan regions? | Yes | |
| Is the species indigenous/endemic to Western Ghats? | ||
| Is the species indigenous/endemic to Eastern Ghats? |
More plants native to India
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
If no maps are displayed below, it means the required data is absent. Click on "Edit with form" button on top of the page to add this information.
{{#generateMap:Andhra Pradesh,Bihar,Chhatisgarh,Gujarat,Jharkhand,Karnataka,Kerala,Madhya Pradesh,Maharashtra,Orissa,Rajasthan,Tamil Nadu,West Bengal|Madhuca_longifolia_brahma.svg|align=center}}
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Does this species have any medicinal use? | Yes |
|
Other plants of the same family having medicinal use:
|
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| General types of ailments this species is used for treating | Infectious diseases, Accidents, Pains and Inflammation, Systemic disorders, Organ-specific disorders | |
| Specific ailments for which the species is used | Snake Bite, Blisters, Bronchitis, Cachexia, Cholera, Cough, Dysuria, Fever, Fistula, Gingivitis, Laxative, Smallpox, Bee sting, Suppuration, Tuberculosis, Wound | Dr.Duke |
| Medicinal systems which use this plant | Ayurveda, Folk Medicine | |
| Details of Medicinal use | ||
| Parts of the plant used for treatment | ||
| Names of some medicinal active compounds in this plant, if known. | ||
| Details of the active chemical compounds found in this plant | ||
| Is the molecular basis of the medicinal action known? | ||
| Details of molecular basis of action | ||
| Are the toxic effects of consumption of this plant known? | ||
| Details of the toxic effects of the plant species | ||
| Have there been validation/clinical studies related to this plant? | ||
| Details of the clinical studies related to the plant species |
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Is this plant/plant-derived product used in food preparations? | Yes | User-reported |
| Part(s) of the plant used in the food preparations | Bark, Leaves, Flower, Fruit | |
| Details of use in food preparations | ||
| Does this species have any religious significance? | ||
| Religions which mention/give significance to this species | Google images, Wikipedia | |
| Religious occasions | ||
| Details of religious use |
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Is this plant cultivated commercially in India? | Yes | |
| Uses for which the plant is commercially cultivated | Human consumption, Medicinal use, Religious use, Wood | |
| Plant parts of commercial value | Root, Stem, Bark, Leaves, Flower, Seeds | NCBI Taxonomy, Wiki |
| Products where this plant is used | User-reported | |
| Description of use | About 30-40 percent of the tribal economy in north India such as in Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Orissa is dependent on the mahua seeds and flowers. The tree has a potential of enhancing rural income. (Hindu)
Madhuca indica (syn. Madhuca latifolia, Bassia latifolia,) is a deciduous tree found in India. It bears edible flowers and fruit. The tree has a spreading root system so can be used to prevent soil erosion. The timber is hard and is used in construction. Bark of the tree is known to have medicinal properties. Seed is rich in oil and has been used in soap and candle making. Seed cake is used as an organic fertilizer. M. indica is being explored as a potential source of biofuel. (NCBI Taxonomy) |
Hindu, NCBI Taxonomy |
| States where this plant is cultivated commercially | Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa | |
| Best period for planting this plant | ||
| Best period for harvesting this plant | ||
| Method of propagation | ||
| Water requirement of this plant | ||
| Pests and Diseases affecting this plant during cultivation | ||
| Other considerations while cultivating this plant |
Pubmed Word cloud
This word cloud is obtained using the tool LigerCat by searching the Pubmed database. LigerCat builds the cloud from the most relevant Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms. Each term's relative size indicates how many times it appears in the PubMed search results. Click on a term to access the full LigerCat cloud, with live PubMed search capabilities. LigerCat has been developed for the Biology of Aging Project.
The page may take some time to load since LigerCat is searching the entire PubMed database and sending us the results in real time.
- If there is an error message below, it means that there is no retrievable information available on NCBI
- If the number of nucleotide sequences is less than 100, very little genomic work has been done on this species. A respectable number of nucleotide sequences is above 10000.
- Most of the nucleotide sequences may come from three sources:
- Studies on single genes, where people try to sequence genes such as some specific dehydrogenases important,say, for tannin production
- Sequences of Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer, whose sequence is used for generating molecular phylogenetic trees to establish species relationships
- Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) which can tell about which genes are present and expressed in the species at a particular time in the given tissue
{{#queryDB:taxonomy |Madhuca longifolia }}
| Parameter | Value(s) | References See complete references in the References section at the end |
|---|---|---|
| Details of modern scientific knowledge available for this species | Very little is known about the DNA/RNA/Proteins of this species. NCBI Taxonomy search on 10 Aug, 2010 revealed just 1 EST and 1 protein sequence, that too from a chloroplast thioesterase gene. However, Nandan Biomatrix Limited is supposed to have undertaken a genome sequencing project.
The seed has a high oil content and the plant is thus being explored as a source of biofuel |
NCBI Taxonomy. |
| Are herbarium specimen available for this species? | ||
| Institutes having herbarium samples |
If nothing is displayed in this section, it means the EoL ID has not been defined. Please click on Edit with form button on top and follow the instructions for filling in the EoL ID
{{#EoLOnlyAdditionalInfo:1155126}}
References
Hindu (Web): Article from The Hindu, Accessdate=2010-08-08
NCBI Taxonomy (Web): NCBI Taxonomy entry on Madhuca, Accessdate=2010-08-10
Dr. Duke (Web): Dr. Duke's ethnobotanical db referenced by GRIN, Accessdate=2010-08-10
| This article is a stub. You can help Project Brahma by expanding it. |


